INSERTION SORT
Insertion sort is based on the idea that one element from the input elements is consumed in each iteration to find its correct position i.e, the position to which it belongs in a sorted array.
It iterates the input elements by growing the sorted array at each iteration. It compares the current element with the largest value in the sorted array. If the current element is greater, then it leaves the element in its place and moves on to the next element else it finds its correct position in the sorted array and moves it to that position. This is done by shifting all the elements, which are larger than the current element, in the sorted array to one position ahead
Implementation
void insertion_sort ( int A[ ] , int n)
{
for( int i = 0 ;i < n ; i++ ) {
/*storing current element whose left side is checked for its
correct position .*/
int temp = A[ i ];
int j = i;
/* check whether the adjacent element in left side is greater or
less than the current element. */
while( j > 0 && temp < A[ j -1]) {
// moving the left side element to one position forward.
A[ j ] = A[ j-1];
j= j - 1;
}
// moving current element to its correct position.
A[ j ] = temp;
}
}
Take array .
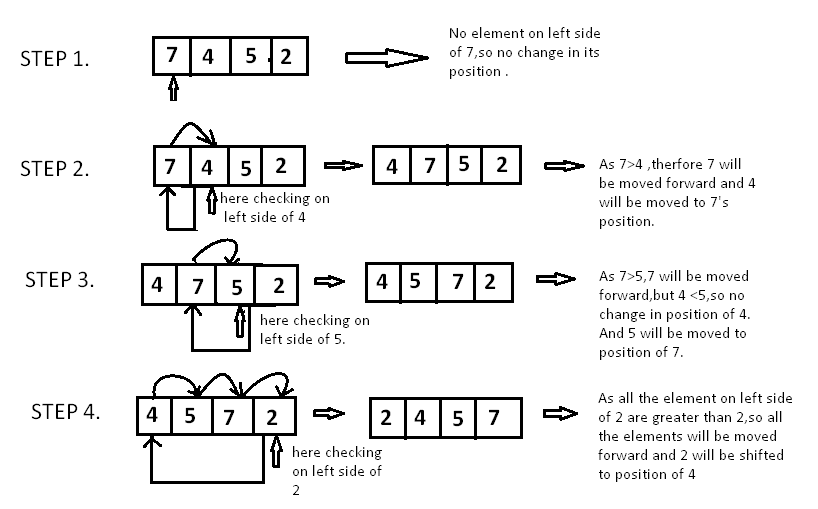
Since is the first element has no other element to be compared with, it remains at its position. Now when on moving towards , is the largest element in the sorted list and greater than . So, move to its correct position i.e. before . Similarly with , as (largest element in the sorted list) is greater than , we will move to its correct position. Finally for , all the elements on the left side of (sorted list) are moved one position forward as all are greater than and then is placed in the first position. Finally, the given array will result in a sorted array.
Time Complexity:
In worst case,each element is compared with all the other elements in the sorted array. For elements, there will be comparisons. Therefore, the time complexity is
No comments:
Post a Comment